Modernizing Legacy Automation Frameworks: When to Migrate & What to Use

As businesses strive for faster releases and higher-quality software and apps, traditional methods may become a hindrance. The cloud-centric, agile pipelines of today are too fast for legacy automation frameworks, which were often designed for monolithic applications or restricted environments. Instead of just being a technical update, modernizing such frameworks is a strategic decision that enables more intelligent testing, increased cooperation, and improved scalability.
What Is Legacy Automation?
It refers to scripts or frameworks that are outdated and were designed using traditional methods, equipment, or technology. Such frameworks may not possess advanced traits to meet the requirements of new-edge development techniques, such as DevOps testing, agile delivery, or mobile-first environments, as they were often created for a specific set of apps or use cases.
Risks of Sticking with Traditional Testing Frameworks
Clinging to legacy automation may seem lucrative in the short term; however, it introduces multiple risks that can hinder extended product quality and launch velocity:
- Inaccurate or Incomplete Test Coverage
- High Maintenance Expenses
- Lack of Integration with CI/CD
- Poor Performance and Adaptability
- Zero Support for Smart or AI Testing
- Compliance and Safety Gaps
What is the Advantage of Legacy Technology in Automation?
Although modernization is essential, legacy technology remains important, especially when combined with standard automated tools or platforms.
One major reward is stability. Legacy systems, particularly those built on older ERP mainframes or environments, often support essential business functions that are expensive or risky to replace rapidly. Advantages comprise:
- Covering the legacy systems’ lifespan with automation.
- Reducing human interference without rewriting core systems.
- Generating a foundation for digital transformation with no business interruption.
- Allowing non-invasive automation across multiple legacy platforms.
SUGGESTED READ - How to build a future-proof test automation architecture?
How to modernize legacy QA frameworks?
Let us find out how to do it:
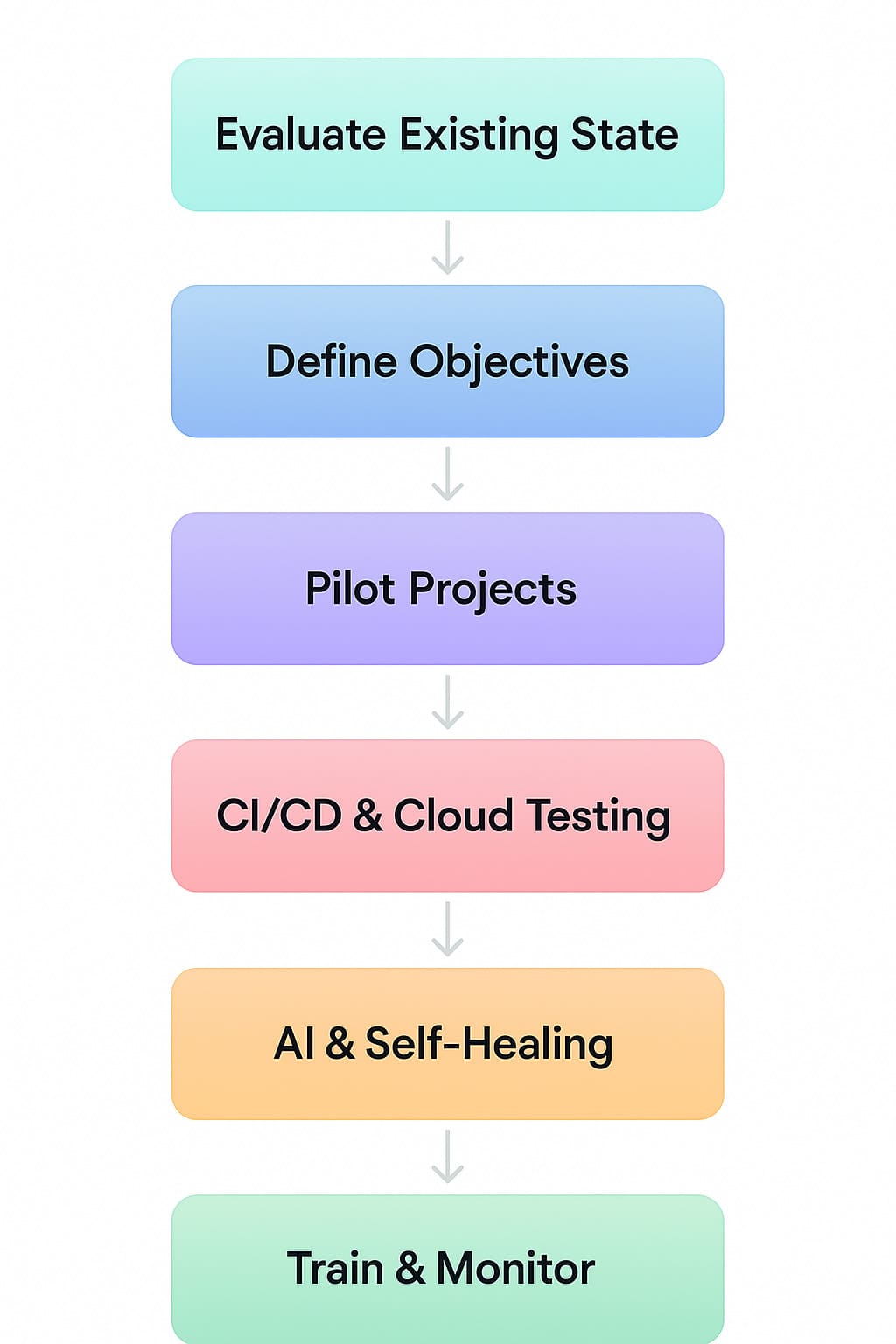
1. Evaluate Your Existing State
Detect what functions & what do not in your legacy setup. Record any gaps in test coverage, technical debt, and integration issues.
2. Define Modernization Objectives
Are you aiming for better scalability? Speedy launch cycles? AI-centric test intelligence? Find your requirements to drive framework & tool choices.
3. Start Small with Pilot Projects
Select a manageable test suite (such as smoke tests) to migrate first. This builds confidence and restricts risk in the new setup.
4. Execute CI/CD & Cloud Testing
Guarantee your new framework blends with CI/CD tools such as Azure DevOps, GitHub Actions, or Jenkins, and supports implementation on cloud-centric platforms.
5. Integrate Self-Healing and Artificial Intelligence
Make use of AI-centric features for self-healing locators, flaky test recognition, and intelligent test selection, to augment test speed & accuracy.
6. Train Teams & Monitor Results
Upskill your team & make use of reporting tools to compute success. Implement iterative improvements to refine your test strategy over time.
Comparison of legacy vs modern automation frameworks
| Feature | Legacy Automation Framework | Modern Automation Framework |
|---|---|---|
| Implementation Speed | Often slow & sequential. | Supports parallel and distributed implementation. |
| CI/CD Integration | Manual or missing. | Built-in integrations with pipelines. |
| Scalability | Restricted to on-premise. | Scalable through cloud and containers. |
| Maintenance | Higher, prone to breakage. | Low, with self-assessment and modular scripts. |
| ML or AI Capabilities | Not accessible. | Supports AI-centric analytics and testing. |
| Support for Cross-platform | Restricted. | Extensive support for API, web, & mobile testing. |
| Ease of Use | Intricate & code-heavy. | Often low-code with reusable elements. |
What to Use: Modern Frameworks Like ACCELQ
Modernizing your legacy automation strategy demands not merely replacing old forms of tools but upgrading to intelligent, flexible test frameworks that support today’s CD goals. One unique solution in this space is ACCELQ, a sophisticated, AI-centric, no-code automated testing platform built for collaboration, speed, and flexibility.
Why ACCELQ?
It is a codeless, cloud-native platform that streamlines API, middleware, and web testing, making it particularly priceless for enterprises juggling intricate, distributed systems. Let us take a glance at the core traits of ACCELQ:
- No-code Test Authoring: Allows both non-tech and tech users to produce dynamic test cases without scripting.
- AI-centric Maintenance: Features NLP and self-healing to reduce manual script maintenance.
- Collaboration-First Design: Back-up agile teams with real-time test planning, implementation monitoring, and change impact scrutiny.
- E2E Web Automation Testing: From API to data layers to User Interface (UI), ACCELQ offers complete automation in a single platform.
- Built-in CI/CD Incorporation: Smoothly blends with other advanced tools such as DevOps, GitHub, Jenkins, and others for continuous testing.
Conclusion
Restructuring or reforming an outdated automation system is a strategic decision that cannot be ignored. The secret to moving toward more intelligent, flexible, and adaptive designs is to keep using what is already effective. Professionals can escape the maintenance trap and focus on providing value by identifying when to migrate, integrating with cloud-based and CI/CD systems, and deploying AI-assisted testing platforms.
Nishan Joseph
VP Sales Engineering
Nishan is a tech strategist with expertise in Test Automation and roles at giants like TCS, Microfocus, and Parasoft. At ACCELQ, he champions Strategic Alliances, cultivating global tech partnerships. Educated at Leeds University and Symbiosis Pune, he also possesses an engineering background from Bangalore.
You Might Also Like:
 The Complete Guide To AI Mobile Testing
The Complete Guide To AI Mobile Testing
The Complete Guide To AI Mobile Testing
 Smart Visual Testing: How to Catch What the Eyes Miss?
Smart Visual Testing: How to Catch What the Eyes Miss?
Smart Visual Testing: How to Catch What the Eyes Miss?
 Migration From TestProject to ACCELQ
Migration From TestProject to ACCELQ

































