TDD vs BDD: Understanding the Differences

Writing code is only one module of the software development process. But thoroughly testing the code to verify that the software meets the essential criteria and standards is challenging for developers. Here comes the role of testing methodologies such as test driven development (TDD) and behavior driven development (BDD). TDD is a method that consists of writing tests before code developing, whereas BDD focuses on defining a system’s behavior through testing.
TDD vs BDD are used commonly and can help developers to overcome the challenges of forecasting user requirements and developing simple tests. While acceptance test driven development (ATDD) is a prominent testing method used to ensure that the code meets the end user’s expectations. These testing methods involve writing tests and time planning to ensure the software development teams understand user requirements and develop quality products. These methods are also used for automated test analysis.
What is TDD vs BDD?
Test-Driven Development is a testing methodology implemented from a developer’s perspective. In this method, a QA engineer starts designing and writing test cases for each small functionality of an application to answer a simple question: Is the code valid? The primary intention of TDD is to write or modify new code only when a test fails. Hence, it results in less duplication of test scripts.
Behavior-driven development (BDD) is a new agile software development methodology in which testers and testing teams write test cases in simple English. This method can revolutionize the software development process by shifting focus to collaboration and shared understanding among teams.
Steps involved in the TDD method
Incorporating TDD into your software development process can significantly improve code quality and reduce defects. By following the iterative cycle of writing a test, developing and refactoring the code, teams can ensure that their software meets its requirements and is adaptable to future changes. Refactoring refers to modifying code without altering its primary functionality or behavior. A structured explanation of the steps involved in TDD is as follows:
| Steps | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Write a test | Create a test for a small part of the functionality. This test should initially fail as the code does not yet exist. |
| Run the test | Execute the test suite to confirm the new test fails, verifying that the functionality is not yet implemented. |
| Implement the code | Write less code required to pass the test. Focus on enough implementation to satisfy the test condition. |
| Run the tests again | Rerun every test, including the new test, to examine if the new code passes and does not break existing functionalities. |
| Refactor the code | Optimize the newly implemented code while maintaining its original functionality. It involves cleaning up code and improving performance. |
| Repeat | Continue these steps for each new feature or part of functionality to build the application with a reliable test suite gradually. |
Steps involved in the BDD method
Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) bridges the space between non-technical and technical stakeholders by using a common language to define software behavior. This methodology emphasizes understanding requirements through scenarios, enabling teams to develop features that align closely with user needs. A structured explanation of the steps involved in BDD is as follows:
| Steps | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Find features | Collaborate with stakeholders to find and prioritize the features required for the software. |
| Writing scenarios | Design user stories and define acceptance criteria in the form of scenarios. Use a common language to describe expected behavior. |
| Reviewing scenarios | Conduct scenario reviews with all stakeholders to ensure clarity and understand the requirements. |
| Implement the code | Developers write code to implement the functionality described in the scenarios, ensuring it meets the acceptance criteria. |
| Writing automated tests | Generate automated tests based on the defined scenarios. It often involves using BDD frameworks. |
| Run the tests | Execute the automated tests to validate that the implemented functionality behaves as expected. |
| Refactor the code | Optimize and clean the code, ensuring that it remains maintainable while retaining the functionality described in the scenarios. |
| Repeat | Continue the BDD cycle for new features or changes, incorporating feedback and necessary new requirements. |
Steps involved in the ATDD method
ATDD is a collaborative approach that involves business analysts, developers, and testers in defining acceptance criteria for user stories prior to development. This methodology confirms that the final product meets the specified requirements and user expectations. A structured explanation of the steps involved in acceptance test driven development is as follows:
| Steps | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Define user stories | Collaborate with stakeholders to write down user stories that describe desired functionality from the user’s perspective. |
| Find acceptance criteria | For each user story, define acceptance criteria that outline specific conditions to be met for the story to be considered complete. |
| Write acceptance tests | Create acceptance tests based on the defined acceptance criteria. These tests should clearly outline the system’s expected behavior. |
| Review and verify tests | Conduct reviews of the acceptance tests with all stakeholders to ensure clarity and agreement on the acceptance criteria and expected outcomes. |
| Implement the code | Developers write the code to implement the functionality illustrated in the user stories and acceptance tests. |
| Execute acceptance tests | Run the acceptance tests to check that the implemented functionality meets the specified criteria. |
| Refactor the code | Review and optimize the code to improve maintainability and performance while ensuring that the acceptance tests still pass. |
| Repeat for new features | Continue the ATDD process for extra user stories or changes, incorporating feedback and necessary new requirements. |
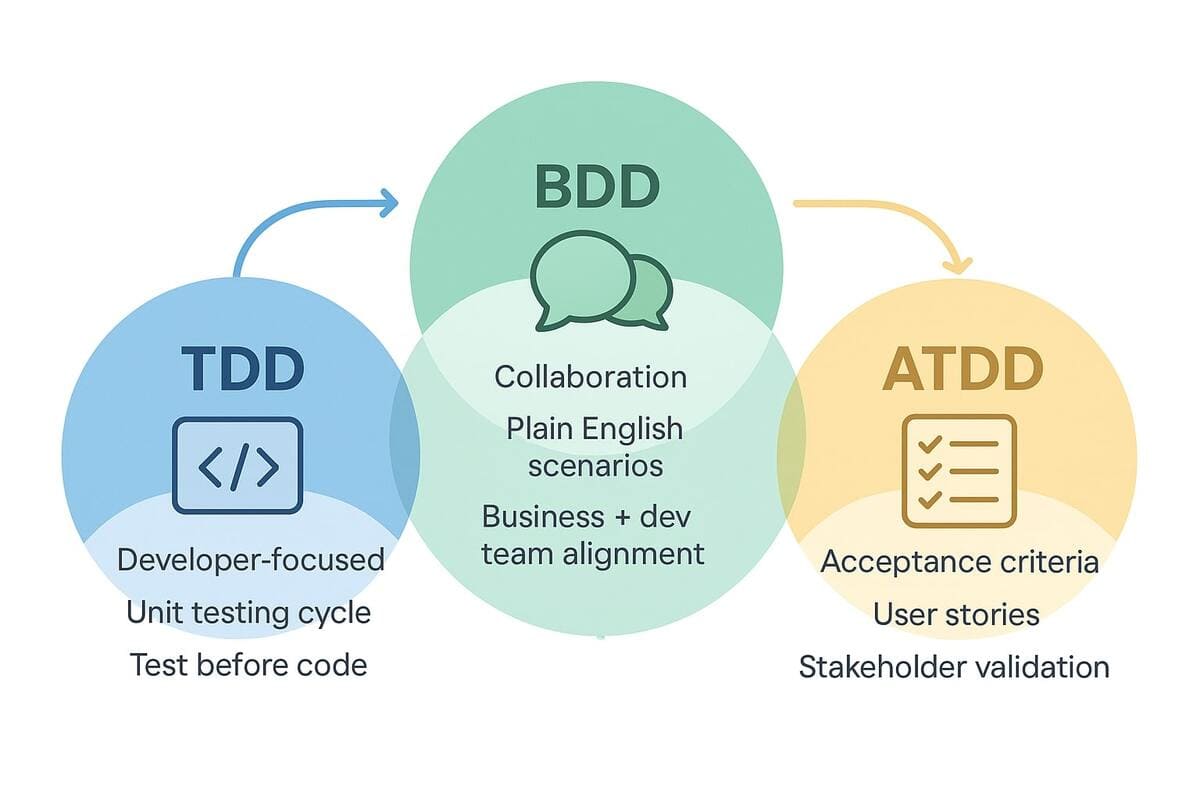
Similarities and differences of BDD vs TDD
When discussing test driven development vs behavior driven development, we must understand their similarities. Both of them intend to lead your software development process for improving usability and maintaining product quality. BDD aims to enhance the collaboration between the development team and the business. TDD employs a continuous testing and coding cycle to list specifications for particular software. The following points discuss the differences between the BDD framework vs TDD:
| Scope | BDD spans a single behavior with a single test. Conversely, TDD spans a minor feature with a single unit test. |
| Documentation | In TDD, unit tests function as technical documentation. It allows only developers to read and understand the tests. But BDD involves writing tests in non-technical language. Since the predicted application behavior is explained in simple English, anyone in your team can understand it. |
| The purpose behind testing | TDD method tests for functionality, whereas the BDD method tests for design logic. |
Quick Recap: ATDD Vs BDD Vs TDD
| Parameters | ATDD | BDD | TDD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Focuses on writing acceptance tests. | Focuses on the correspondence between implemented features and expected behavior. | Focuses on developing the required functionality based on test cases. |
| Who can be involved? | Only technical teams, like development teams, can be involved | Involves customers, business analysts, testers, developers, and more. | Involves business analysts, testers, developers, and more. |
| Development stages | Feature discussion, acceptance criteria creation, testing, implementation, and code refactoring. | Feature discussion, scenario creation, testing, implementation, and code refactoring. | Test creation, implementation, and code refactoring |
| Main stages | Writing acceptance tests is the main stage in ATDD. | Discussion and scenario creation are the main stages in BDD. | Test case development is the main stage in TDD. |
| Level of implementation | Easy to implement | Easy to implement, making BDD a high-level implementation with regard to test case development. | Low-level to implement |
| Tool | FitNesse | ACCELQ | JUnit |
Which one to opt for between TDD, BDD, and ATDD?
The following points provide a perspective on which one to choose:
- TDD is more suitable for projects that don’t involve APIs or servers.
- BDD is more suitable for e-commerce projects.
- ATDD is more suitable for working on developing app projects.
It may seem complex to implement a specific development method from scratch. A combination of all three or only two provides outstanding opportunities for conversations, collaboration, and enough insights into the final product specifications. Hence, meticulously choosing the right method based on your project’s requirements and anticipated outcomes will save time overall in the product development process.
Conclusion
The goal of comparing TDD, BDD, and ATDD isn’t to choose one over the others, but to understand which methodology fits the current phase of your project and the challenges you face. When applied thoughtfully, these methods enable you to develop high-quality software that meets both user needs and business objectives.
Platforms like ACCELQ simplify the adoption of TDD and BDD by allowing test logic to be created directly within the scenario-building process. You can define new Actions on the fly, supporting a top-down development approach. This seamless workflow reduces context-switching and makes it easier to implement TDD effectively within the software development lifecycle. As well as, ACCELQ’s agile testing framework ensures that BDD testing is in sync with agile development processes, maintaining pace with rapid development cycles.
Geosley Andrades
Director, Product Evangelist at ACCELQ
Geosley is a Test Automation Evangelist and Community builder at ACCELQ. Being passionate about continuous learning, Geosley helps ACCELQ with innovative solutions to transform test automation to be simpler, more reliable, and sustainable for the real world.
You Might Also Like:
 Mastering the Essentials: 7 Key fundamentals of software testing
Mastering the Essentials: 7 Key fundamentals of software testing
Mastering the Essentials: 7 Key fundamentals of software testing
 Is Your App Ready for the European Accessibility Act?
Is Your App Ready for the European Accessibility Act?
Is Your App Ready for the European Accessibility Act?
 Cheatsheets every Tester Should Know.
Cheatsheets every Tester Should Know.
































