15 Types of Software Testing Every QA Must Know About

Software testing, as you might already know, is a fundamental part of SDLC (software development lifecycle). It helps us to ensure that the software we develop functions as expected and meets all the quality standards before it is released.
Whether you're new to software testing or have been doing it for years, software testers must be up-to-date about the latest software testing methodologies to ensure quality software development.
We have listed 15 different types of testing methods and classified them into three main categories first. Also, explain when to use each method depending on your software project.
Let’s look at the types of software testing for each category in detail.
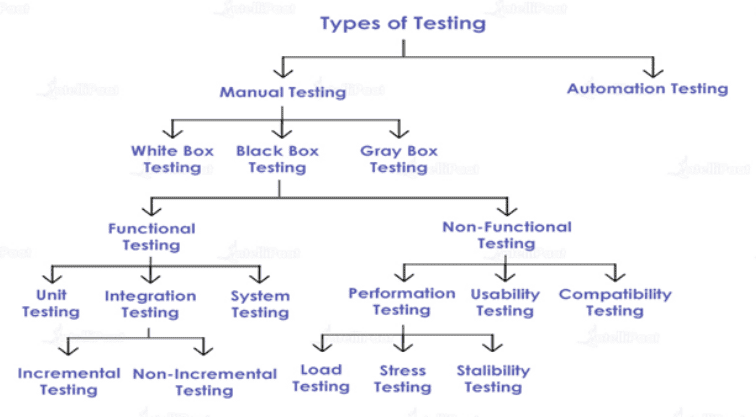
Functional Software Testing
Functional software testing types help testers validate that the features of the software being developed are working as expected using the following methods.
1. Unit Testing
Unit testing is one of the core functional testing types that provides the foundation for verifying software behavior.
To elaborate, unit testing focuses on testing the functionality of individual units or components of code in isolation to verify each part operates correctly on its own.
Compared to other types of testing, the scope of unit tests is quite small and focuses mostly on validating things like
- Correctness of a single function or method
- Individual classes meet the requirements
- Logic within a specific module
Developers usually do unit testing by writing various test cases to test their code. It helps them catch bugs early during coding before issues can multiply, saving the time and effort of dedicated software testers.
Example:
- Input: Giving different email addresses where valid emails are accepted and invalid ones are rejected.
- Execution: Run the feature with each email address.
- Verification: Check if the valid emails are accepted and failed ones are rejected.
Purpose: This example demonstrates integration testing by focusing on how different system components (the e-commerce platform and the payment gateway) work together.
2. Integration Testing
Unlike unit testing, integration testing helps testers determine whether different modules or services work together harmoniously as intended.
That means after developers have conducted and verified that individual units are working properly, software testers combine those units and perform integration tests to test them as a group.
Specifically, integration testing helps check if the interface connections between units are working and verify that the integrated system meets the requirements.
This process helps to confirm that the units tested by developers independently are operating together when integrated.
Example:
- Input: Adding products to the cart and making the payment through the payment gateway.
- Execution: Perform a complete transaction from selecting a product to completing payment.
- Verification: Ensure that the e-commerce platform correctly communicates with the payment gateway and the transaction is processed smoothly without any issues.
3. System Testing
System testing, as the name suggests, basically helps to evaluate the entire system and checks that it meets the overall functional requirements of the software application.
To verify this, this software testing method focuses on end-to-end business processes and workflows to test and confirm that the system is functioning as expected and intended.
To perform a system test, software testers need to perform the following:
- Testing system functionality using actual production-like data
- End-to-end testing of transactions and data flows
- Testing of reporting features and data validation
- Testing integrations with external systems/interfaces
- Testing system performance under load close to production
- Security testing at a system level
After performing these tests, system testing finally gives testers the confidence that the overall solution will function as needed when it is finally deployed in the live environment.
Example:
- Input: Execute a series of actions – searching & selecting a flight, entering passenger details, making a payment, and receiving a booking confirmation.
- Execution: Run through the entire process from start to finish, simulating a real user’s experience.
- Verification: Check that the flight search, booking process, payment gateway, and confirmation system work together seamlessly and the entire process is completed without errors.
Purpose: This example illustrates system testing by focusing on the entire airline reservation system. It assesses the system’s overall functionality, ensuring it meets its intended requirements and specifications.
4. Acceptance Testing
Acceptance testing helps software testers confirm that the software meets all agreed business and user requirements and is acceptable for delivery.
This is done by testing the software application with the following three acceptance testing sub-types:
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT) – Business users test the system against user requirements to validate usability, workflows, accessibility, and behavior.
- Business Acceptance Testing – Confirms the solution aligns with business processes and that outputs/reporting meet needs.
- Regulatory Acceptance Testing – Validates adherence to applicable laws, regulations, standards, and compliance mandates.
Unlike other functional testing types, acceptance testing is usually conducted in a production-like environment to thoroughly examine whether the software meets all validation criteria and is ready for go-live.
Example:
- Input: Key users from the company, such as project managers and team members, use the software to manage a mock project. This includes creating projects, assigning tasks, tracking progress, and generating reports.
- Execution: The users perform all the functions they typically use daily, assessing the software’s usability, features, and performance.
- Verification: Gather feedback from these users to determine if the software meets their needs and expectations and if it’s ready for deployment in the work environment.
Purpose: This example demonstrates acceptance testing by focusing on how the end-users interact with the software and whether it fulfills their requirements and expectations.
Non-Functional Testing
Non-functional testing of every software is equally important as functional testing because these tests help us evaluate aspects like performance, security, usability, and reliability.
Here are the four most important non-functional testing types every software tester needs to know about.
5. Performance Testing
In layman’s terms, performance testing helps to check how fast the software performs under various conditions.
To elaborate, it mainly examines the overall responsiveness, stability, resource usage, and even scalability under both - normal & peak - conditions.
Like acceptance testing, performance testing also has sub-types that software testers must perform to evaluate the software.
- Load testing – Checks system behavior under increasing normal load.
- Stress testing – Subjects the system to peak loads and evaluates robustness.
- Spike testing – Simulates sudden large spikes in user load.
- Endurance testing – Validates system performance over time under sustained usage.
- Scalability testing – Tests performance with data volumes scaled up.
These individual sub-tests help software testers identify the possible breaking points in the software and ensure that the software can handle the projected production loads.
In a nutshell, the performance sub-tests help to find bottlenecks, memory leaks, or software defects that could cause slow response times or could result in system crashes.
Example:
- Input: Simulate many users accessing the website simultaneously, performing various actions like browsing products, adding items to the cart, and checking out.
- Execution: Using automation testing tool to generate virtual traffic and monitor how the website handles the increased load, focusing on page load times, transaction processing speed, and system stability.
- Verification: Analyze the performance data to identify issues like slow page loading or transaction failures during peak traffic.
Purpose: This example illustrates performance testing by evaluating how well the e-commerce website operates under stressful conditions.
6. Security Testing
As you can already guess, security testing allows software testers to identify vulnerabilities that could allow hackers to penetrate and compromise confidential data.
To prevent this, software testers need to conduct various security tests as described below:
- Penetration testing – Simulates attacks to exploit security gaps.
- Vulnerability scanning – Uses automated tools to detect weaknesses.
- Fuzz testing – Inputs invalid data to find failures.
- Risk assessments – Analyzes architecture and design for risks.
Performing these different security tests will help you establish strong security and prevent any potential vulnerabilities that could lead to cyber-attacks, data breaches, and compliance violations.
As a software tester, it is imperative to learn how to conduct these tests to mitigate any security risks in your application.
Example:
- Input: Conduct various security tests, including penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and checking for SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and other standard security threats.
- Execution: Simulate potential cyber-attack scenarios to assess how well the application can withstand malicious attempts to access sensitive data or disrupt services.
- Verification: Analyze the results to identify any security weaknesses or vulnerabilities that must be addressed to prevent security breaches.
Purpose: This example demonstrates security testing by focusing on the robustness of the online banking application against potential cyber threats.
7. Usability Testing
Usability testing is more accessible for most software testers as it mainly involves evaluating how easy the application interface is for the end users.
To elaborate, the goal of usability testing is to check if any issues with navigation, controls, and the overall visual design of your software application could negatively impact the user experience.
To conduct successful usability tests, you need to learn to observe representative users carrying out tasks in your software application. This will help you to discover their pain points and opportunities to improve the UI design of your software.
Example:
- Input: Recruit actual or representative app users and ask them to perform various tasks, such as searching for products, adding items to the cart, navigating through different sections, and checking out.
- Execution: Observe the users as they interact with the app, noting any difficulties or confusion they encounter, and gather their feedback on the app’s layout, design, ease of navigation, and clarity of instructions.
- Verification: Analyze the observations and feedback to identify areas of the app that need improvement to enhance user satisfaction and ease of use.
Purpose: This example illustrates usability testing by focusing on the end-user experience of the mobile shopping app.
8. Compatibility Testing
It is a must-have part of any software testing strategy because it helps to check and verify that your software application is functioning correctly across all target operating systems, browsers, devices, and software versions.
In layman’s terms, it helps software testers confirm that their software automatically and successfully adjusts and displays correctly across various devices, platforms, and configurations.
If you want to enhance your skillset as a software tester, learning how to conduct compatibility testing is critical for ensuring a consistent user experience in your application.
Example:
Scenario: Ensuring a video streaming service works effectively across different devices and browsers.
- Input: Test the streaming service on various devices (like smartphones, tablets, laptops), operating systems (Windows, macOS, Android, iOS), and web browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge).
- Execution: On each device and browser, check for proper functioning of key features like video playback, audio synchronization, user interface elements, and responsiveness.
- Verification: Identify compatibility issues, such as videos not playing on a specific browser or interface glitches on a particular device.
Purpose: This example demonstrates compatibility testing by focusing on how well the video streaming service operates across various hardware and software environments.
Other Types of Software Testing
Apart from the functional and non-functional testing methods, a few other software testing types are worth learning.
9. Ad-hoc Testing
Unlike most functional and non-functional testing types, the Ad-hoc testing method takes an informal approach to validating software.
This software testing method does not rely on predefined test cases. Instead, software testers usually create dynamic tests on the fly based on their knowledge and experience.
Thanks to this, software testers can quickly identify defects generally missed by formal testing methods. The flexibility of ad-hoc testing allows you to be reactive and test things you didn’t initially plan for.
Plus, as you conduct ad-hoc tests across multiple projects, you’ll soon develop the intuition and skills to perform ad-hoc testing effectively over time.
Example:
Scenario: Randomly testing various features of a social media application without any specific plan or test cases.
- Input: Explore different app functionalities, such as creating posts, commenting, liking, sharing, navigating through profiles, and using search functions.
- Execution: Interact with the app in an unstructured manner, trying out various features randomly and attempting to use them in unconventional ways.
- Verification: Note any unexpected behaviors, bugs, or crashes during this exploratory process.
Purpose: This example illustrates ad-hoc testing by focusing on the spontaneous and unscripted exploration of the social media app. It helps uncover issues that might not be found through structured testing methods, providing insights into the app’s robustness and user experience under less predictable conditions.
10. Back-end Testing
Back-end testing focuses on validating all the behind-the-scenes components that power the front-end application users interact with.
It aims to ensure all the behind-the-scenes functionality works correctly before the software goes live.
In a nutshell, performing rigorous back-end testing is critical for every software tester to catch severe defects and improve the stability as well as the performance of the final product.
Example:
- Input: Examine critical back-end operations such as database updates when a booking is made, server response times, data retrieval for booking history, and payment processing.
- Execution: Perform actions on the front end (like making a booking) and monitor how the back end processes these actions, ensuring data is correctly stored, retrieved, and updated in the database.
- Verification: Check for any issues in data handling, server performance, or integration points between the front-end and back-end systems.
Purpose: This example demonstrates back-end testing by focusing on the server-side components of the online booking system.
11. Backward Compatibility Testing
This software testing type helps check and validate whether the newly developed or launched software works well with the older environment version.
Why is this important? - Many companies have old, legacy systems and data the software needs to interact with. But sometimes, upgrading to a new version could create problems with these legacy pieces. This is exactly where backward compatibility software testing helps by preventing these issues from developing in the first place.
For example, say you upgrade an HR system to a new version. Backward compatibility testing would validate:
- Old employee data from the legacy system can still be imported and read by the new system.
- The new system can still connect and share data with old financial or payroll systems.
- Any features or workflows from the legacy system will continue working in the new version.
- This confirms that legacy systems and data will function after the upgrade. It verifies no backward “incompatibilities” were introduced that would break legacy integration.
Without solid backward compatibility testing, upgrades risk unknowingly damaging connections to old systems still in use.
This software testing method helps to manage and prevent issues when transitioning between software versions.
Example:
- Input: Use files (like documents, spreadsheets, and presentations) created in previous software versions.
- Execution: Open, edit, and save these files in the new version of the software. Test various features like formatting, macros, and embedded elements to see if they work as expected
- Verification: Confirm that the new version opens and edits the old files without issues and maintains all functionalities and formatting.
Purpose: This example illustrates backward compatibility testing by focusing on the software’s ability to function seamlessly with files and data created in older versions.
12. Maintenance & Regression Testing
Maintenance and regression testing are practices that validate that software continues to function correctly after changes.
Maintenance testing is conducted on modified or enhanced software to ensure new features or bug fixes do not unintentionally affect the overall functionality.
Regression testing is mostly about re-running test cases you have developed on previous versions of the software whenever updates are made. The goal of regression testing is to check and ensure that existing functionality did not break as a result of maintenance changes.
Example:
Scenario: Testing an updated version of a corporate Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system to ensure new updates haven’t adversely affected existing functionalities.
- Input: After updates or bug fixes are made to the CRM system, run a series of predefined tests that cover all the critical functionalities of the system, such as customer data management, interaction tracking, and report generation.
- Execution: Perform these tests to ensure that new changes have not introduced any new bugs and that all existing features are functioning as expected.
- Verification: Identify any areas where the recent changes might have caused issues or degraded the performance of existing functionalities.
Purpose: This example demonstrates maintenance and regression testing by focusing on the stability and reliability of the CRM system after updates or modifications.
13. Mobile App Testing
Tests software applications designed to run on mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets.
It involves UI/UX, functional, security, compatibility, performance, and network traffic testing to validate the mobile application's overall usability, functionality, and reliability across all intended devices and conditions.
As a software tester, you must make sure that the app is easy and intuitive to navigate on smaller screens, works without any issues across different phone models, and, most importantly, double-check that it keeps your users’ data safe and secure.
The main goal is to remove any glitches or frustrations before people download your app and ensure smooth performance and great user experience so that your users keep coming back.
Example:
Scenario: Testing a fitness tracking app across various mobile devices and operating systems.
- Input: Install the app on smartphones and tablets with various screen sizes and operating systems (like IOS & Android).
- Execution: Test critical features of the app, such as step counting, workout logging, calorie tracking, synchronization with wearable devices, and data visualization.
- Verification: Ensure the app functions correctly on all devices, providing accurate tracking, a responsive interface, and a consistent user experience.
Purpose: This example illustrates mobile app testing by focusing on the app’s performance and usability across a wide range of mobile devices and operating systems.
14. API Testing
API testing is about ensuring these API connections work as expected. It involves mimicking how an actual application would interact with an API and validating that the API behaves correctly.
API testing helps you to test things like:
- Can our application successfully connect to the API?
- Does the API return the expected data structures and values?
- How does the API handle errors or large volumes of requests?
- Can our application successfully connect to the API?
- Does the API return the expected data structures and values?
- How does the API handle errors or large volumes of requests?
API testing aims to uncover issues, including bugs, performance problems, or security vulnerabilities before the API goes live in production. Furthermore, It mitigates the risks of deploying buggy or vulnerable APIs that could cause widespread problems.
Comprehensive API testing is indispensable for building stable, scalable, secure software applications.
Example:
- Input: Test the APIs responsible for fetching flight options, hotel availability, booking confirmations, and payment processing.
- Execution: Send requests to these APIs and analyze the responses for correctness, format, latency, and error handling. This includes checking if the flight and hotel data is up-to-date, the booking process is correctly executed, and payments are securely processed.
- Verification: Ensure the APIs are reliable, return the expected data, handle errors gracefully, and meet performance benchmarks.
Purpose: This example demonstrates API testing by focusing on the functionality, reliability, and performance of the APIs used by the travel booking service.
15. Automated Testing
Last but not least, automated testing refers to test processes that run automatically without direct human input. It involves using various testing tools to automate the execution of tests on a software application.
The best part? - You can automate many of the functional & non-functional testing types, such as unit testing, integration testing, regression testing, acceptance testing, and more.
Scenario: Testing the APIs of a travel booking service that integrates with various airlines and hotels.
- Input: Develop automated test scripts that cover various website functionalities, such as user registration, product search, adding items to the cart, checkout process, and payment.
- Execution: Run these automated tests at scheduled intervals or after every major code update to the website. The tests are executed without manual intervention, checking for issues or bugs.
- Verification: Analyze the results of the automated tests to identify any failures or areas of concern that need to be addressed.
Purpose: This example illustrates automated testing by focusing on using software tools to test the online retail website’s functionalities repeatedly. l
Quick Recap - Comparison of Software Testing Types
| Software Testing Types | Description |
|---|---|
| Functional Testing | Validates intended behaviors and functionality from a user’s perspective. |
| Unit Testing | Tests individual code components in isolation early in development. |
| Integration Testing | Tests interactions between integrated modules after unit testing. |
| System Testing | End-to-end validation of the entire system to meet requirements. |
| Acceptance Testing | Confirms system acceptability by end users like UAT (user acceptance testing). |
| Non-Functional Testing | Validates non-functional aspects like performance, security, etc. |
| Performance Testing | Tests behavior under expected and peak workloads. Load/stress testing done. |
| Security Testing | Identifies vulnerabilities and weaknesses compromising security. |
| Usability Testing | Evaluates ease of use and navigation from a user perspective. |
| Compatibility Testing | Validates working across environments, browsers, devices, etc. |
| Other Software Testing Types | Specialized testing types that can’t be part of functional and non-functional testing categories. |
| Ad-hoc Testing | Unplanned exploratory testing without test cases. |
| Back-end Testing | Validates server-side components and logic. |
| Regression Testing | Retests the existing features after modifications. |
| Mobile App Testing | Validates functionality, UI/UX, etc. on mobile devices. |
| API Testing | Validates application programming interfaces meet specs. |
| Automated Testing | Testing is done using automation tools and frameworks. |
What’s the Ideal Software Testing Approach for Your Project?
While we covered a lot of ground by looking at 15 different software testing types, you still need to figure out which are ideal for your software project.
Hopefully, this post will serve as a helpful starting point as you explore which software testing strategies are right for your specific needs.
Remember, testing is not just about finding bugs - it is an indispensable process for building trust and confidence in your software products. Therefore, you must think about software testing holistically across the entire development lifecycle and employ a diverse toolkit of complementary testing methods.
ACCELQ, a comprehensive test automation platform, has proven itself to be a game-changer in streamlining and enhancing the software testing process. With its innovative features and capabilities, testing teams can achieve higher efficiency, accuracy, and agility in their testing efforts.
Geosley Andrades
Director, Product Evangelist at ACCELQ
Geosley is a Test Automation Evangelist and Community builder at ACCELQ. Being passionate about continuous learning, Geosley helps ACCELQ with innovative solutions to transform test automation to be simpler, more reliable, and sustainable for the real world.
Related Posts
 Practical Ways to Get Better at Software Testing
Practical Ways to Get Better at Software Testing
Practical Ways to Get Better at Software Testing
 Understanding the Software Testing Life Cycle: Beginner’s Tutorial
Understanding the Software Testing Life Cycle: Beginner’s Tutorial